January 4, 2019 Updated Guidelines on Patentable Subject Matter
The USPTO has released its January 4, 2019 Updated Guidelines on Patentable Subject matter.
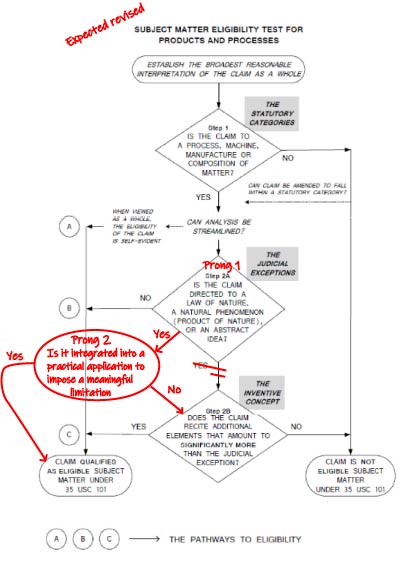
Although most of the previous 2 step patent eligibility analyses does not change, the guidelines present another pathway to analyze claims for patent eligibility when the claims include abstract ideas and products or laws of nature (natural phenomenon). Step 2a has been revised into Prong One and Prong Two. Prong 1 is much the same as previous Step 2a, except now, a claim will only be considered to be directed to an abstract idea if it includes mathematical concepts, certain methods of organizing human activity, or mental processes. The definition of laws of nature or natural phenomenon does not change. If a claim is found to be directed to an abstract idea or natural phenomenon, it will be further analyzed in Prong Two to see if the abstract idea or natural phenomenon is intergraded into a practical application so as to impose a meaningful limitation. If the answer is Yes, the claim is patent eligible. If the answer is No, the analysis continues as before in Step 2b.
A nonexclusive list of additional elements to be considered in Prong Two are those that:
- Reflect an improvement in the functioning of a computer
- Apply a particular treatment or prophylaxis for a disease
- Implement a judicial exception in conjunction with a particular machine or manufacture that is integral to the claim
- Transform a particular article to a different state
- Apply the element in some meaningful way that does not just monopolize the exception.
While some of these elements are the same as those in Step 2b, Step 2b excludes elements that are well-understood, routine, conventional activity, whereas Step 2a does not. Revised Step 2a allows examiners to determine that a claim is patent eligible because a judicial exception has been integrated into a practical application, whether or not additional elements are conventional or well known.
The flow chart in MPEP 2106 has not yet been updated but, given the new Guidelines, I expect changes to be more or less as follows: